Eight new sites inscribed on UNESCO’s World Heritage List

The World Heritage Committee meeting in Krakow since 2 July today inscribed cultural sites in Denmark, France, Germany, Iran, Poland, and the Russian Federation, along with one that spans Croatia, Italy and Montenegro, AVA Diplomatic reports.
The sites added, in order of inscription are:
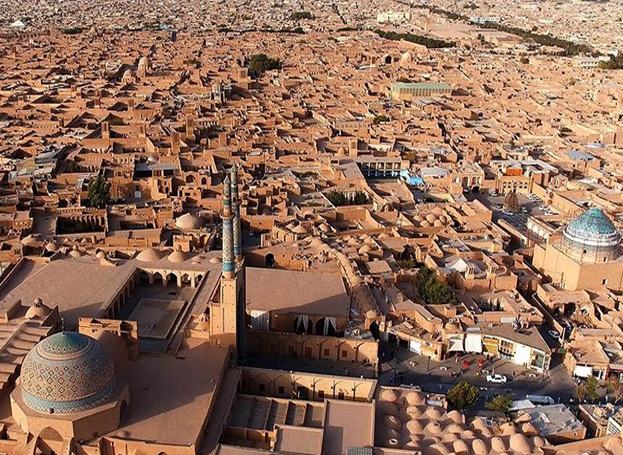
Historic City of Yazd (Islamic Republic of Iran)
The City of Yazd is located in the middle of the Iranian plateau, 270 kilomtres southeast of Isfahan, close to the Spice and Silk Roads. It bears living testimony to the use of limited resources for survival in the desert. Water is supplied to the city through a qanat system developed to draw underground water. The earthen architecture of Yazd has escaped the modernization that destroyed many traditional earthen towns, retaining its traditional districts, the qanat system, traditional houses, bazars, hammams, mosques, synagogues, Zoroastrian temples and the historic garden of Dolat-abad.
Sacred Island of Okinoshima and Associated Sites in the Munakata (Japan)
Located 60 km off the western coast of Kyushu island, the island of Okinoshima is an exceptional example of the tradition of worship of a sacred island. The archaeological sites that have been preserved on the Island are virtually intact, and provide a chronological record of how the rituals performed there changed from the 4th to the 9th centuries CE. In these rituals, votive objects were deposited as offerings at different sites on the Island. Many of them are of exquisite workmanship and had been brought from overseas, providing evidence of intense exchanges between the Japanese archipelago, the Korean Peninsula and the Asian continent. Integrated within the Grand Shrine of Munakata, the island of Okinoshima is considered sacred to this day.
Venetian Works of Defence between the 16th and 17th Centuries: Stato da Terra – Western Stato da Mar (Croatia, Italy, Montenegro)
This property consists of 15 components of defence works in Italy, Croatia and Montenegro, spanning more than 1,000 kilometres between the Lombard region of Italy and the eastern Adriatic Coast. The fortifications throughout the Stato da Terra protected the Republic of Venice from other European powers to the northwest and those of the Stato da Mar protected the sea routes and ports in the Adriatic Sea to the Levant. They were necessary to support the expansion and authority of the Serenissima. The introduction of gunpowder led to significant shifts in military techniques and architecture that are reflected in the design of so-called alla modernaI bastioned, fortifications, which were to spread throughout Europe.
Kujataa Greenland : Norse and Inuit Farming at the Edge of the Ice Cap (Denmark)
Kujataa is a sub-arctic farming landscape located in the southern region of Greenland. It bears witness to the cultural histories of the Norse hunters-gatherers who started arriving from Iceland in the 10th century and of the Norse farmers, Inuit hunters and Inuit farming communities that developed from the end of the 18th century. Despite their differences, the two cultures, European Norse and Inuit, created a cultural landscape based on farming, grazing and marine mammal hunting The landscape represents the earliest introduction of farming to the Arctic, and the Norse expansion of settlement beyond Europe.
Taputapuātea (France)
Taputapuātea on Ra’iatea Island is at the centre of the “Polynesian Triangle,” a vast portion of the Pacific Ocean, dotted with islands, and the last part of the globe to be settled by humans. The property includes two forested valleys, a portion of lagoon and coral reef and a strip of open ocean. At the heart of the property is the Taputapuātea marae complex, a political, ceremonial and funerary centre. It is characterized by a paved courtyard with a large standing stone at its centre. Widespread in Polynesia, the marae were places where the world of the living intersects the world of the ancestors. Taputapuātea is an exceptional testimony to 1,000
Caves and Ice Age Art in the Swabian Jura (Germany)
Modern humans first arrived in Europe 43,000 years ago during the last ice age. One of the areas where they took up residence was the Swabian Jura in southern Germany. Excavated from the 1860s, six caves have revealed items dating from 43,000 to 33,000 years ago. Among them are carved figurines of animals (including cave lions, mammoths, horses and cattle), musical instruments and items of personal adornment. Other figurines depict creatures that are half animal, half human and there is one statuette of a female form. These archaeological sites feature some of the oldest figurative art worldwide and help shed light on the origins of human artistic development.
Tarnowskie Góry Lead-Silver-Zinc Mine and its Underground Water Management System (Poland)
Located in Upper Silesia, in southern Poland, one of the main mining areas of central Europe, the site includes the entire underground mine with adits, shafts, galleries and water management system. Most of the site is situated underground while the surface mining topography features the remains of the 19th century steam water pumping station, which testifies to continuous efforts over three centuries to drain the underground extraction zone. It has made it possible to use undesirable water from the mines to supply towns and industry. Tarnowskie Góry represents a significant contribution to the global production of lead and zinc.
Assumption Cathedral and Monastery of the town-island of Sviyazhsk (Russian Federation)
The Assumption Cathedral is located in the town-island of Sviyazhsk and is part of the monastery of the same name. Situated at the confluence of the Volga, the Sviyaga and the Shchuka rivers, at the crossroads of the Silk and Volga routes, Sviyazhsk was founded by Ivan the Terrible in 1551. It was from this outpost that he initiated the conquest of the Kazan Khanate. The Assumption Monastery illustrates in its location and architectural composition the political and missionary programme developed by Tsar Ivan IV to extend the Moscow state. The cathedral’s frescoes are among the rarest examples of Eastern Orthodox mural paintings.
The 41st session of the World Heritage Committee (9-12 July), chaired by Jacek Purchla, founder and director of the International Cultural Centre in Kraków, will continue inscribing sites on the World Heritage List this afternoon.